Early recognition of depression in children and adolescents through identifying persistent irritability, mood swings, concentration issues, changes in appetite/sleep patterns, and social withdrawal is crucial. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and evidence-based therapeutic options like individual/group psychotherapy and mindfulness meditation are effective in addressing negative thought patterns and building resilience. Considering gender identity issues during adolescence in mental health assessments is vital as societal pressure or transphobia can contribute to depression. Access to tailored therapy, lifestyle adjustments including exercise and mindfulness, and keeping a Mental Wellness Journal empower young individuals to maintain emotional well-being and recognize early signs of depression.
Depression is a growing concern, especially among children and adolescents. This article delves into crucial strategies for prevention, focusing on early recognition of signs and symptoms, tailored therapy options for those with diverse gender identities, and proactive measures to build resilience. We explore how lifestyle changes and professional guidance can foster well-being, emphasizing the importance of accessible support for all, particularly in navigating unique mental health challenges associated with gender identity.
- Recognizing Depression in Children and Adolescents: Early Signs and Symptoms
- Gender Identity and Mental Health: Navigating Unique Challenges and Supportive Therapy Options
- Preventative Measures: Building Resilience and Fostering Well-being Through Lifestyle Changes and Professional Guidance
Recognizing Depression in Children and Adolescents: Early Signs and Symptoms

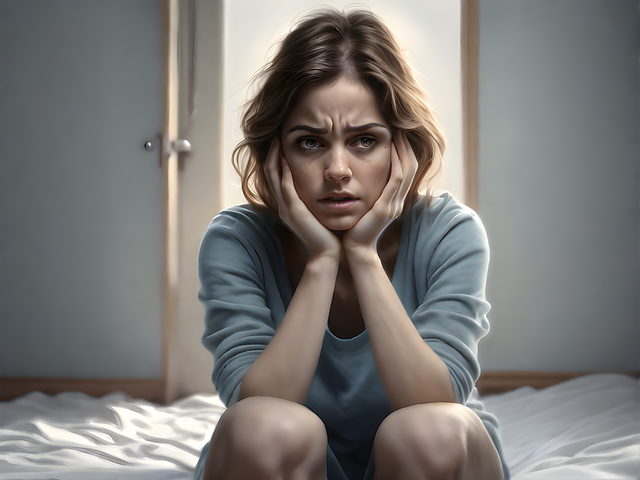
Recognizing depression in children and adolescents is a crucial step in ensuring timely intervention and support. While adults may exhibit clear signs of sadness or loss of interest, young individuals often express their distress through more subtle changes in behavior. Early signs can include persistent irritability, mood swings, difficulty concentrating, and changes in appetite or sleep patterns. Adolescents might also withdraw from social activities they once enjoyed, experience a drop in academic performance, or engage in risky behaviors as a means of coping. It’s essential for parents, caregivers, and mental health professionals to foster mental health awareness by recognizing these early indicators.
Therapy for children and adolescents can be highly effective in addressing depression. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), for instance, helps young people identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors contributing to their low mood. Gender identity issues, a significant aspect of adolescent development, may also play a role in mental health concerns. Mental health professionals should conduct a thorough risk assessment to understand the unique challenges faced by each individual. By promoting inner strength development through therapy, support systems, and education, we can empower children and adolescents to navigate their emotional well-being effectively.
Gender Identity and Mental Health: Navigating Unique Challenges and Supportive Therapy Options

The relationship between gender identity and mental health is a complex and often overlooked aspect of depression prevention. Individuals navigating their gender identity, especially children, face unique challenges that can significantly impact their mental wellness. The pressure to conform to societal norms or struggle with internalized transphobia can lead to heightened stress levels and contribute to the risk of depression.
Supportive therapy options, such as individual or group psychotherapy, are instrumental in fostering resilience building and mindfulness meditation practices. These therapeutic approaches provide safe spaces for individuals to explore their identities, process difficult emotions, and develop coping strategies. By integrating evidence-based techniques, therapists can help individuals enhance their mental wellness, build a positive sense of self, and cultivate the skills needed to navigate societal challenges associated with gender identity expression.
Preventative Measures: Building Resilience and Fostering Well-being Through Lifestyle Changes and Professional Guidance

Depression prevention strategies begin with building resilience and fostering well-being. Lifestyle changes play a significant role in mental wellness; regular exercise, for instance, boosts mood by increasing brain chemicals like serotonin and norepinephrine. Additionally, mindfulness meditation helps individuals cultivate present-moment awareness, thereby reducing anxiety and stress. Keeping a Mental Wellness Journal can also be therapeutic, providing an outlet to process emotions and track progress over time.
Professional guidance is another crucial component. Therapy for Children, including those exploring their gender identity, offers safe spaces to discuss challenges and develop coping mechanisms. Crisis intervention guidance equips individuals with tools to navigate difficult situations, while mindfulness techniques taught by professionals enhance overall mental resilience. These preventative measures collectively empower people to maintain good mental health and recognize early warning signs of depression.
Depression prevention is a multifaceted approach, especially when considering the unique challenges faced by children and adolescents, particularly those navigating gender identity issues. By recognizing early signs, implementing lifestyle changes, and accessing professional guidance such as therapy for children, we can build resilience and promote well-being. Incorporating these strategies into our communities fosters a supportive environment that empowers young individuals to thrive and cope with mental health challenges effectively.